The vagus nerve, or vagus in medical terminology, is the longest cranial nerve, running through the ear and neck to the chest and abdomen. Due to its vast extent, the vagus governs vital organs, including the heart, brain, and lungs, and also plays an important role in the relationship between the spleen, intestines, brain, and inflammation processes.
The main function of the vagus nerve is the regulation of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) - the part of the nervous system that controls the autonomic (involuntary) functions of the body, such as breathing, digestion, and heartbeat.
The ANS has two branches: the sympathetic system, which activates the reactions of mobilization, tension, stress (“fight or flight”), and the parasympathetic system, which controls the relaxation functions (“rest and digestion”). Their balance is reflected in the indicators of heart rate variability, which can be calculated from the electrocardiogram data.
The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work in a complementary way. When the organism in a state of stress activates the sympathetic system, the tone of the parasympathetic response decreases, and vice versa. Therefore, activation of the parasympathetic system during chronic stress (which underlies all diseases) by acting on the vagus leads to an improvement in the state of health in many diseases.
Previously, only surgical stimulation of the vagus nerve by implanting the stimulator inside the body was used for this purpose. In 1997, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of this method for the treatment of epilepsy, and in the 2000s for the treatment of depression and eating disorders. However, due to inconvenience, the possibility of technical complications and side effects, such as pain, coughing, hoarseness, this method has not found wide application.
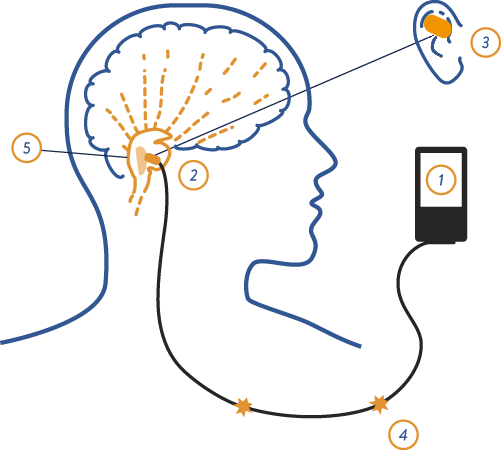
Revolutionary was the discovery of a non-surgical (non-invasive) method of vagus stimulation - through the skin in the area of the outer ear, where a small area of the surface is innervated by one of its branches. It turned out that stimulation of this area of the ear produces effects similar to the surgical method.
It turned out that even one session of this treatment (transcutaneous auricular electrical vagus nerve stimulation - aRLS, taVNS) can significantly improve heart rate variability compared to control treatment, which indicates its ability to increase parasympathetic tone. In addition, the use of aSBN for 15-30 minutes daily for two weeks leads to improvements in depression scores, sleep quality, and other aspects of quality of life.
The vagus nerve projects directly to serotonergic and noradrenergic neurons in the brain, which are associated with many neuropsychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety. Therefore, its electrical stimulation provides a direct modulating effect on the subcortical areas of the brain and leads to changes in the excitability of the cortex. ARS has been shown to attenuate sympathetic arousal associated with stress related to traumatic memories and also reduce symptoms in patients with PTSD, thereby having a beneficial effect on the neurophysiology underlying PTSD.
The use of aSBN can be especially useful in the elderly, since aging is associated with a change in the functions of the autonomic nervous system and is characterized by an increase in sympathetic and a decrease in parasympathetic nervous activity. These autonomic changes can negatively impact heart function, emotions, mood, and gut function, and may play a role in age-related disease.
The method is painless, effective and safe. Patients feel comfortable during the procedure, experiencing only a “tingling” sensation at the site of stimulation. Its effectiveness has already been shown not only in epilepsy and depression, but also in heart failure, inflammatory processes, Alzheimer's disease, obesity, chronic pain and tinnitus (tinnitus).
Guided by the principles of integrative, holistic medicine, combining electrical stimulation of the vagus with psychotherapy, infusions of ketamine and hydroxybutyrate, transcranial electrical stimulation, rehabilitation of the brain "Neurohelp", body-oriented therapy and art therapy, a significant improvement in the health of patients can be achieved.
